JF-0530B Solenoid EN
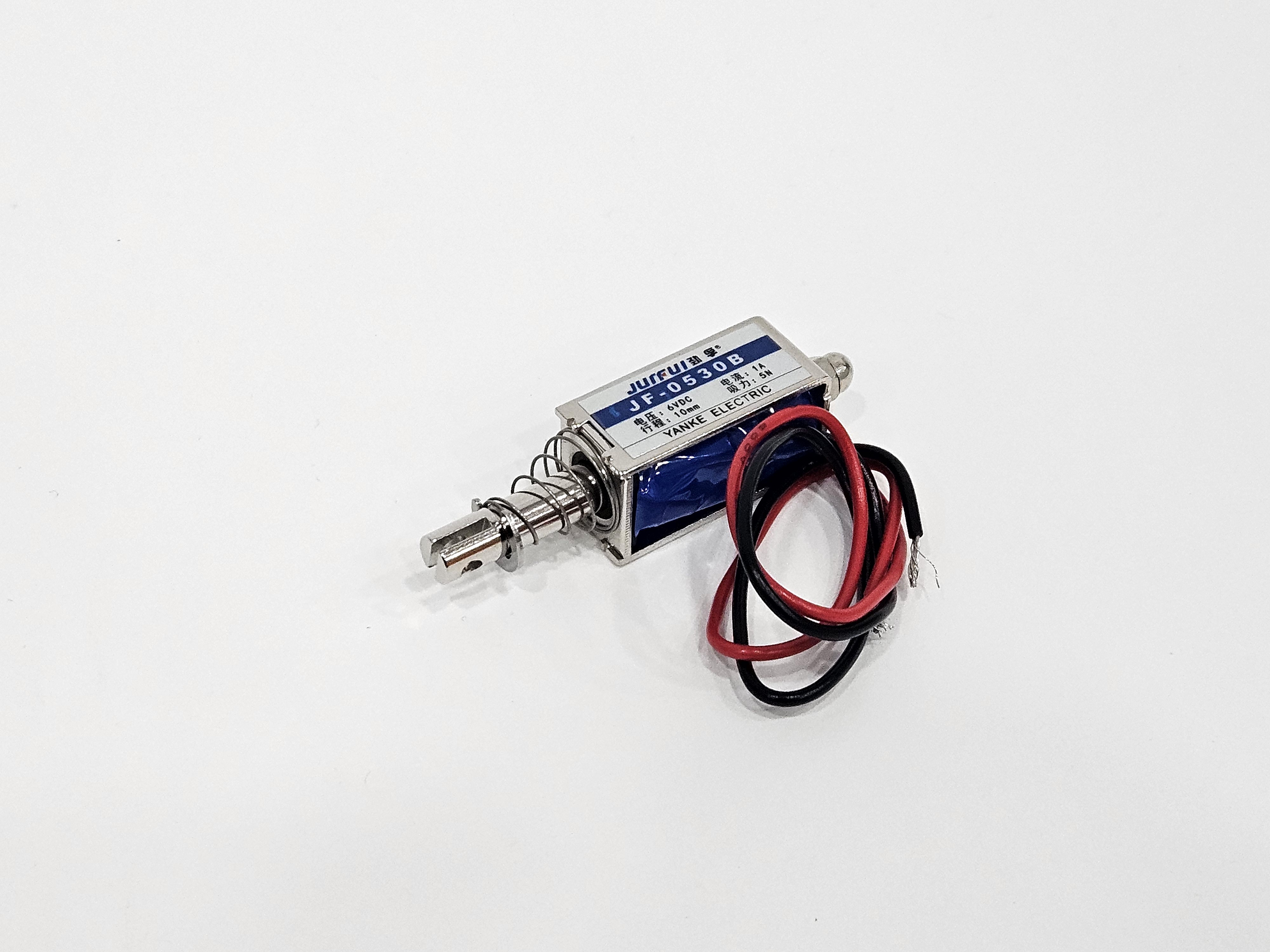

Overview
The JF-0530B solenoid is a device that converts electrical signals into mechanical motion, using the principle of electromagnetic induction.
When current flows, the iron core moves forward due to the magnetic field, and when the current is cut off, the iron core returns to its original position by the spring.
Working Principle
It is composed of a coil that generates a magnetic field when current flows. When current passes through the coil, a magnetic field is formed, and the movable iron core inside moves accordingly. This process generates mechanical motion (linear motion), and when the power is turned off, the iron core automatically returns to its original position.
Specifications
| Size | (Body) 30.1 x 13.2 mm / Including iron core approximately 61mm |
| Voltage | 6V, 12V, etc. In this example, the 6V model is used. |
| Type | Push & Pull |
Example Usage
It is difficult to supply the current required to operate the JF-0530B solenoid directly from the Arduino's digital pins.
To solve this, we use a Relay Module or MOSFET to safely control the current.
Be careful as the solenoid may heat up if operated for long periods of time with short intervals.
Difference Between Relay and MOSFET
MOSFETs consume less power during switching, and since they are electronically controlled switches, they operate much faster than relays.
Moreover, they do not have mechanical parts, which gives them a longer lifespan compared to relays that require physical movement.
However, relays can handle higher voltages or currents and are more suitable when electrical isolation is needed between the Arduino and devices.
Therefore, it is best to select and use them appropriately based on the situation.
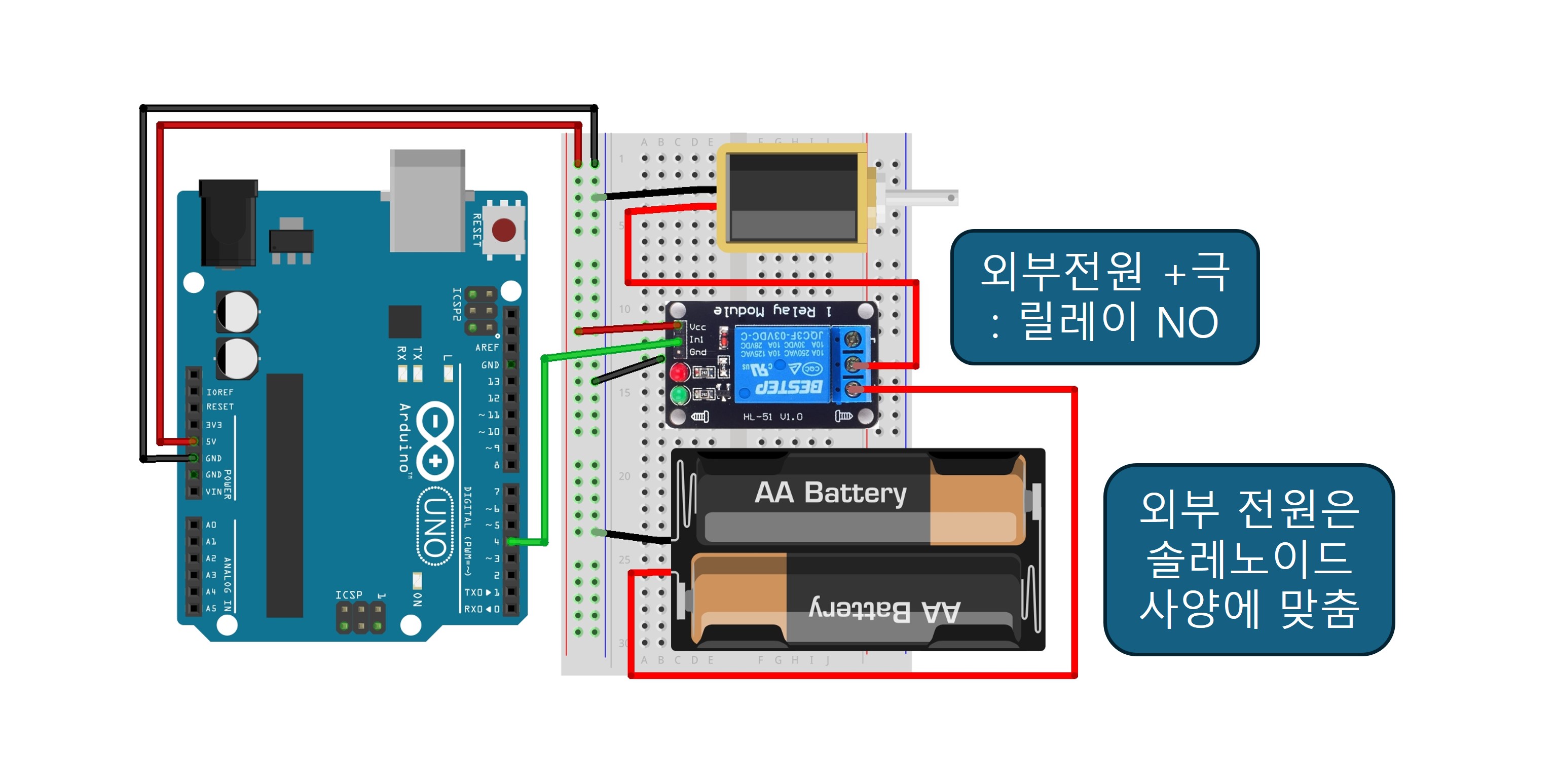
1. Using Relay Module
Circuit Configuration
| Arduino | Relay | Solenoid | External Power |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5V | VCC | ||
| GND | GND | Black wire | Black wire or negative terminal |
| D4 | INI | ||
| COM | Red wire | ||
| NO | Red wire or positive terminal |
Example Code
const int relay = 4;
void setup() {
pinMode(relay, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(relay, LOW);
delay(3000);
digitalWrite(relay, HIGH);
delay(3000);
}
Execution Result
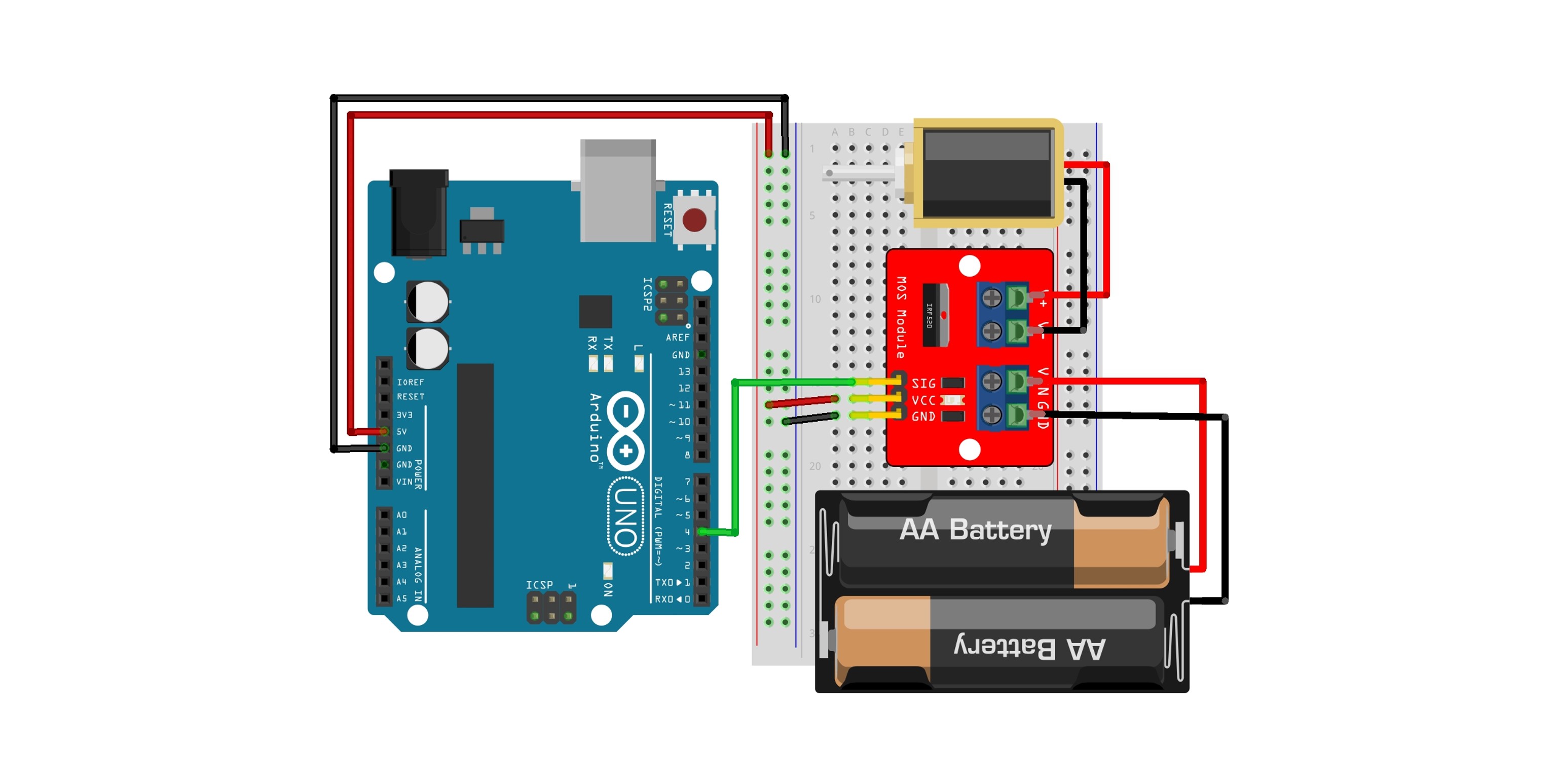
2. Using MOSFET
Circuit Configuration
| Arduino | MOSFET | Solenoid | External Power |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5V | VCC | ||
| GND | GND | ||
| D4 | SIG | ||
| COM | |||
| NO | |||
| Vin | Red wire or positive terminal | ||
| GND | Black wire or negative terminal | ||
| V+ | Red wire | ||
| V- | Black wire |
Example Code
const int mosfet = 4;
void setup() {
pinMode(mosfet, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(mosfet, LOW);
delay(3000);
digitalWrite(mosfet, HIGH);
delay(3000);
}
Execution Result